The US healthcare industry is a complicated system of interconnected activities and organizations. The legal and technological environment entailing the healthcare industry is continuously evolving. When medical billing used to be done on paper, often doctors or their assistants did the complete paperwork themselves. However, with changes in US healthcare laws, electronic health records (EHR) became almost a necessity for healthcare providers, which in turn led to the emergence of specialized medical billing services in the US.
Importance of Medical Billing
There are some organizations which are still using the paper-based systems, but they are at a substantial competitive disadvantage. Furthermore, due to an aging US society and the disease becoming more and more complicated, clinics and hospitals are becoming jam-packed with patients. Not only do doctors and their support staff do not have time to delve into the complicated medical billing process, but it is also not a job of multitasking office assistants anymore. Neither can organizations afford to hire specialized staff and technology needed to do the medical billing in-house.
Medical billing is the process of collecting fees for medical services. Photo Credit: Shutterstock
Thus, many clinicians and most large hospitals are outsourcing medical billing and coding functions to specialized third parties. These medical billing companies have made considerable investments in custom-made certified EHR technology and retain full-time specialized staff that processes tons of claims on a daily basis. It enables them to reduce the inefficiencies that creep up into the in-house medical billing.
Top Things To Know About Medical Billing
Let’s learn about the five most important things you need to know about medical billing services:
Medical Coding and Medical Billing Are Not the Same Thing
While the terms “medical billing” and “medical coding” are often merged, they are not the same thing. Further, coding is done first, and billing comes later in the process.
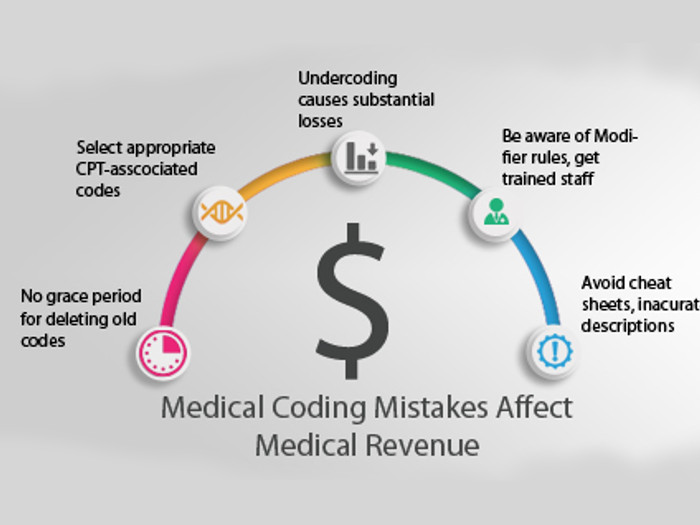
Medical coding is a process which deals with assigning standard codes to the various diagnosis and procedures performed by health service providers. It is done per ICD-10-CM or ICD-10-PCS coding systems developed by the WHO and modified by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services ( [1]CMS) and National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS).
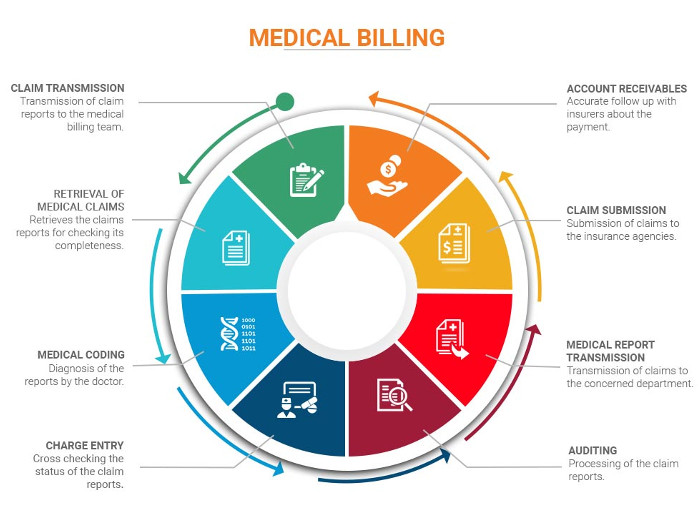
Medical billing, on the other hand, is a process in which medical claims are forwarded to the payers to receive payment for the services provided. Medical billers apply the pertinent prices for each treatment and procedure according to Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) and Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS) code requirements.
Registration & Confirmation of Financial Responsibility
The processing of medical claims may span over just a few days to several months. On occasions, there are numerous forward and backward movements in the process, and this can occur due to errors in the initial registration and confirmation. Therefore, patient verification and authorization is a crucial step that may be performed on every visit. The primary objective of patient verification is to confirm financial responsibility for the medical services performed. Insurance coverage and plans differ significantly from carrier to carrier depending on the state and the premiums paid. Many healthcare providers hire medical billing and coding service providers to utilize their state-of-the-art technology and to avoid costly errors. [2]
Understanding medical billing Photo Credit: Shutterstock
HIPAA Code Set Requirements
While the HIPAA law eradicated all custom-made and local code set requirements and standardized most of the medical data, this does not eliminate all of the complexity of the system. The US-modified version of ICD-10 contains over 70,000 unique codes for disease, symptoms, abnormal findings, and various internal and external causes of injuries or illness. The complexity can be made clear from the following list of code set requirements mandated by HIPAA Law:
• Health Care Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS)
• Current Procedural Terminology (CPT)
• National Drug Codes (NDC)
• The Code on Dental Procedures and Nomenclature (CDT)
• International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems, 10th Edition, Clinical Modification and Procedure Coding System (ICD-10-CM, ICD-10-PCS)
With so many code-set requirements, claims forwarded to the insurance providers are occasionally returned due to missing codes or incorrect data. It can be overcome by hiring professional medical billers who specialize in filing clean claims.
MIPS Score & Physician Compare Initiative
Medical billing services are not only about filing claims for the services delivered. Under the Quality Payment Program (QPP), the Merit-based Incentive Payment System (MIPS) score also depends on the medical billing records. A MIPS score can increase or decrease claim reimbursements by 5% in 2018, which will grow to 9% by 2022. It doesn’t stop here, however.
CMS has announced that it will publish MIPS scores and physician ratings based on those scores on its physician-compare website. This means that people now have better access to information related to the quality of health care service provided by a particular physician or a physician group. This will lead to better healthcare service and drive down prices as patients value reputable physicians more than those with lower ratings. [3]
Agile providers of medical billing services use advanced analytical tools to help their clients to balance between getting a good MIPS score and making the investment on system needed for reporting.

The medical billing process is a process that involves a third-party payer. Photo Credit: Shutterstock
Days in AR & Medical Billing
“Days in AR” is a financial ratio found by dividing the total account receivables for a certain period by the average daily sales for a certain year. It’s also termed as a DSO ratio. It is believed by financial experts that a DSO ratio of more than 60 is dangerous for the financial health of an organization. Good medical billing companies strive to achieve DSO ratio of less than 30.
