Jaggery and sugar are two common sweeteners used throughout the world. Although both are obtained from the same sources, they are much different in their properties and benefits.
Just as twins are different in many respects; jaggery and sugar, made from the same sugar cane juice, are different from one another. These differences must be kept in mind for their proper use.
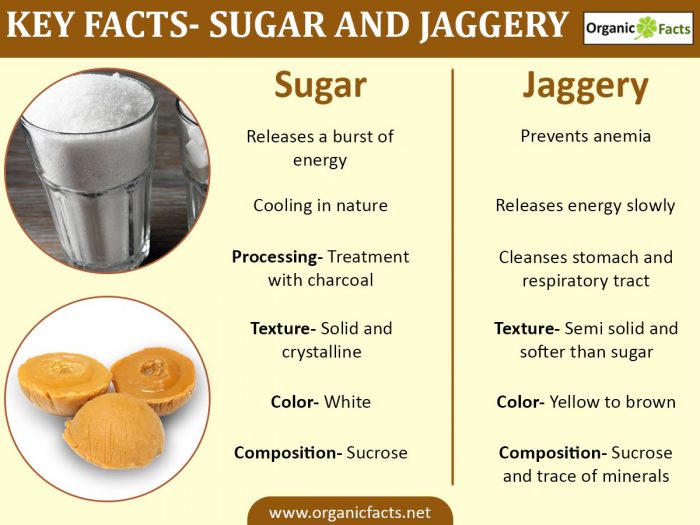
Difference between Jaggery & Sugar
Let us have a look at some of the differences.
Color
- Sugar typically has a bright white color.
- Jaggery shows true Eastman colors, ranging from golden yellow to golden brown, brown, dark brown, and like the color of dark chocolate, depending upon the extent to which it is cooked.
Texture
- Sugar is solid, hard, and crystalline.
- Jaggery is semi-solid, softer than sugar, and amorphous.
Processing
The first stage of the manufacturing of jaggery and sugar is the same. This first step is the boiling of sugar cane juice. However, it changes from that point, which is explained below.
- In the case of sugar, after the initial boiling, the syrup is treated with charcoal (preferably bone charcoal) to absorb unwanted particles and give a clear, transparent solution. This solution, when condenses and crystallizes, results in the formation of sugar.
- In the case of jaggery, there is no treatment with any kind of charcoal, nor there is any kind of crystallization. The syrup is boiled continuously until it is formed into a thick paste. It is then poured into molds to make blocks of jaggery of the desired quantities.
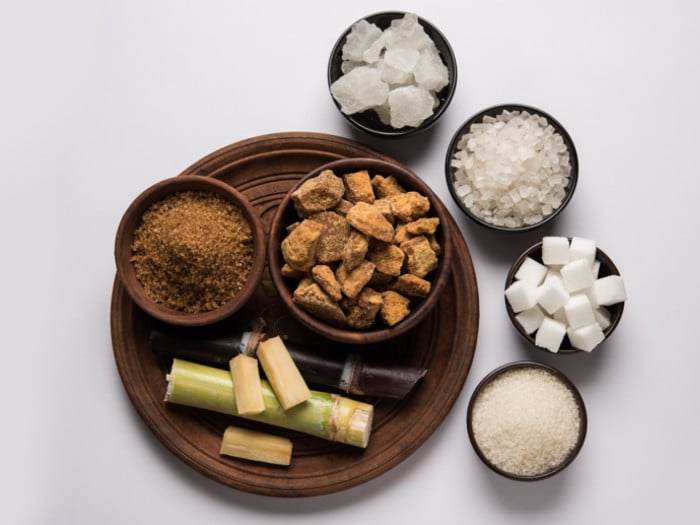

Jaggery vs sugar is a tough battle as both are high on fructose. Photo Credit: Shutterstock
Composition
Both jaggery and sugar are predominantly made up of sucrose, but there are some differences.
- Sugar is made up of only sucrose (C12H22O12).
- Jaggery is predominantly made up of sucrose (C12H22O12), with traces of mineral salts, iron, and some fiber.
Health Benefits
- Being one of the simplest available forms of sucrose, sugar is instantly absorbed in the blood and releases a burst of energy. This may prove harmful to organs such as the kidneys, eyes, and brain, particularly for patients with diabetes. [1]
- Jaggery is far more complex than sugar, as it is made up of long chains of sucrose. Hence, it takes time to digest. This may provide energy for a longer time and is not harmful to the body. However, this does not certify it as fit for consumption by diabetics, because ultimately, it is sugar. Jaggery also contains iron, which is good for health, particularly for those who are anemic or lack iron. Again, jaggery may also contain traces of mineral salts which are very beneficial for the body. You might have experienced this when consuming jaggery, it leaves a hint of salt on the tongue. These salts come from the sugar cane juice where it is absorbed from the soil. Furthermore, jaggery is known to be a very good cleansing agent. It cleanses the lungs, stomach, intestines, esophagus, and respiratory tracts. Those who face dust in their day-to-day life are highly recommended to take a daily dose of jaggery. This can keep them safe from asthma, cough, cold, and congestion in the chest. [2] [3]
Cultural Aspects
- Sugar is believed to have been used in Polynesia by people, and eventually, making its way to India.
- Jaggery has an important place in Indian culture and also in the culture of any country where it is made, probably because it is indigenous. In India, it is offered to gods and goddesses and is used in many religious ceremonies because it is considered holy, as it does not involve any use of bone charcoal.
Industrial Aspects & Marketing
- The sugar industry is very organized and highly mechanized. As almost all the sugar coming into the market is manufactured in sugar mills run by big companies. Hence, sugar is branded and it may have a big influence on the CPI and thus on the economy.
- Jaggery manufacturing has been practiced for centuries much before sugar came into being. This industry is still not organized and out of the realms of the rural areas despite huge demand. Most of the jaggery comes from remote places and reaches the market through agents. Unlike sugar, jaggery is known by the place of its manufacture and not by its brand.
Culinary & Industrial Uses
- Sugar is found in almost every sweet thing. The whole of the sugar-boiled confectionery industry is dependent on sugar. It is used in bakery items like bread, cakes, biscuits, cookies, and other products. Sugar is included in sorbets, syrups, jams, jellies, sauces, marmalade, squashes, soft drinks, packed fruit juices, sweetened milk, milk chocolates, ice creams, ice candies, condensed milk, and this list can go on infinitely. It is also used in some medicines. Sugar is caramelized and mixed with a number of food items and drinks, including alcoholic beverages, to add taste, color, and aroma.
- Jaggery is used in curries, lentil soup, and other preparations. It is an integral part of the country’s sweets made by combining ground nuts, grams, sesame seeds, rice flakes, puffed rice, popped rice, cashew nuts, almonds, wheat, and gram flour snacks with jaggery. These sweets are extensively consumed during winter all over India as they provide nutrition and warmth to combat cold. There is one big industrial use of jaggery in the manufacturing of alcoholic beverages, particularly rum. Rum, in many cases, is made by fermenting jaggery.
Difference between sugar and jaggery Photo Credit: Shutterstock
Availability
- Sugar is available almost anywhere in the world now, except the dense forests of the Amazon, parts of Africa, and Mt. Everest. Availability is never a problem with sugar. Just reach out your hand and you can probably find it.
- If you are not living in a country where jaggery is manufactured, it might be very difficult to find. It contains a lot of moisture, often melts on heating, and contracts fungal infections quite easily. For this reason, it is exported to very few countries from where it is produced. Still, you may be able to get your hands on some if you search for shops that keep Indian or Asian food items. Date palm jaggery and Palmyra jaggery are even more rarely available than Sugarcane jaggery; the reason is a very limited production.
This was a comparative analysis of jaggery and sugar. Those who have not tasted jaggery yet, it won’t hurt to try. You will love its great taste and impressive health benefits.
